Advanced Technologies for Mine Water Management
The rapidly evolving landscape of water in mining has prompted the adoption of a wide range of advanced mine water management technologies. These solutions help mining companies address regulatory, operational, and environmental challenges cost-effectively and sustainably. Below is an overview of key technologies currently shaping the future of mine water management, along with several additional approaches not previously detailed:
1. Mechanical Evaporation with Minetek
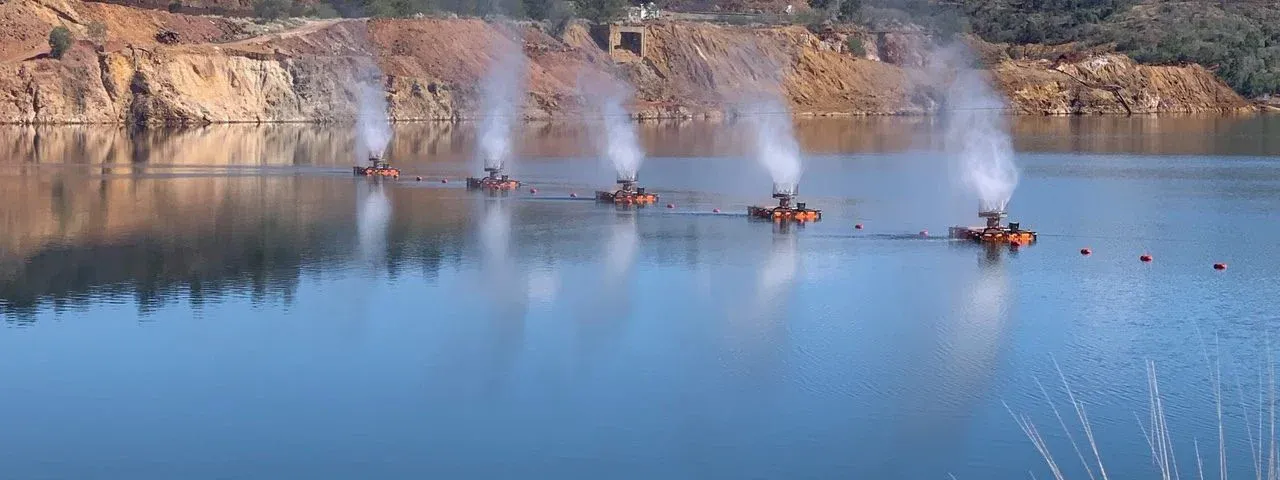
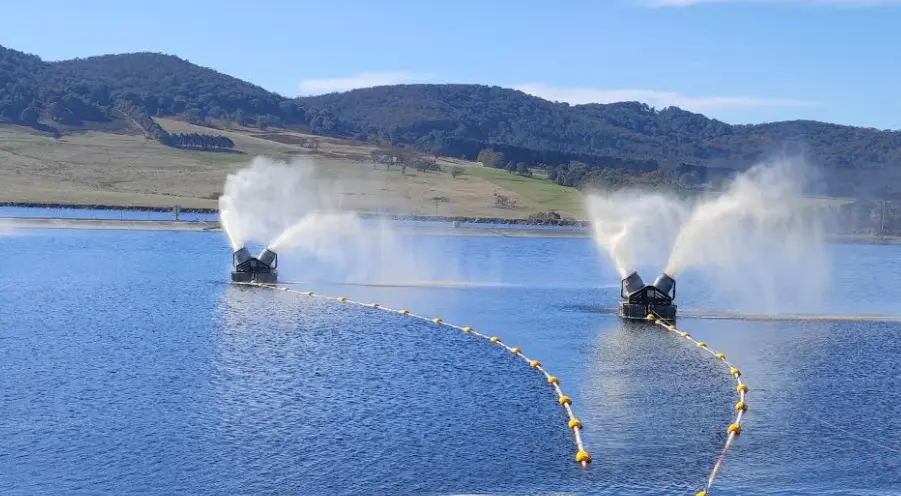
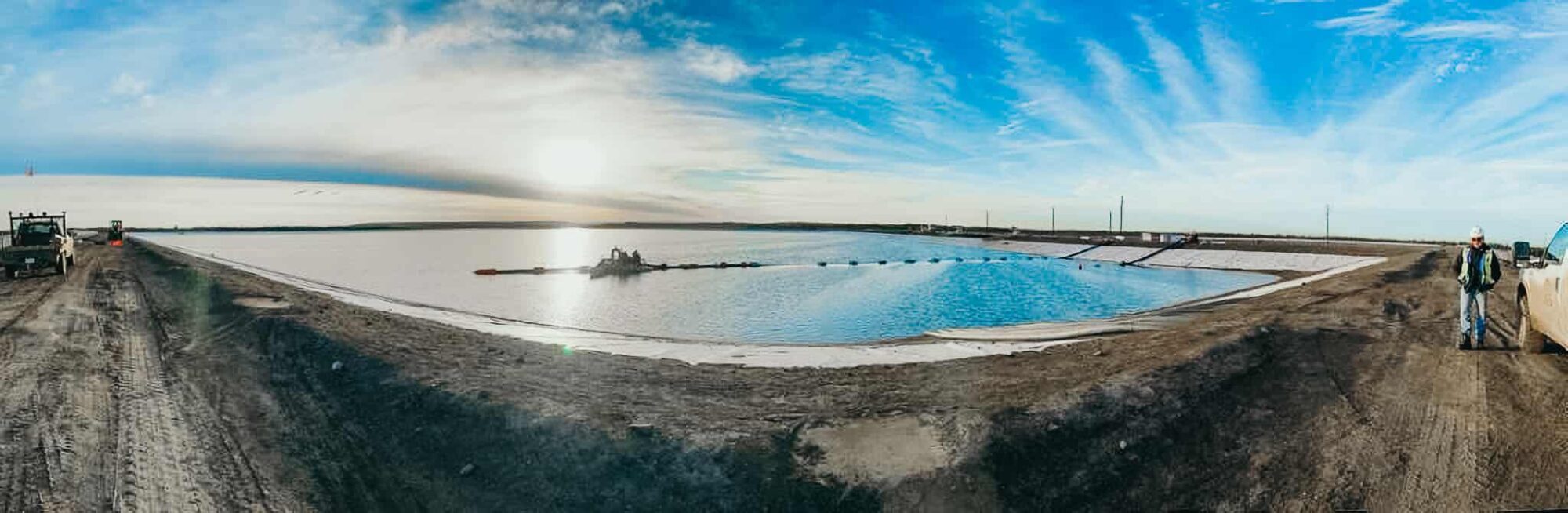
Minetek’s mechanical evaporation technology is a game-changer for managing mine water. Engineered using the first principles of fan engineering and airflow with patented low-fouling nozzles and high-velocity airflow, it processes water with high total dissolved solids (TDS) and total suspended solids (TSS) across a pH range of 1.8 to 14. Unlike solar evaporation ponds, Minetek’s systems are mobile, require minimal maintenance, and operate effectively in diverse climates, from Canada’s winters to Australia’s arid conditions. They process more than 2,160 m³/hour and are not susceptible to changes in feed water quality. The in-built Environmental Management System (EMS) monitors and responds to environmental condition changes like humidity, rain, and wind in real time, optimising operation according to a broad range of adjustable parameters, including optimum sun-up/ downtimes, relative wind speed and direction, humidity and temperature, system water flow, and pressure. With over 700 systems deployed across 29 countries, Minetek’s technology reduces costs by up to 10 times compared to traditional methods.
2. Passive Treatment Systems
Passive treatment technologies use natural processes to remediate mine water, particularly for acid mine drainage (AMD). Constructed wetlands, anaerobic bioreactors, and limestone drains can effectively remove metals and neutralize acidity with minimal energy input and operational oversight. These systems are especially valuable for remote or legacy mine sites, providing long-term, low-cost water quality improvements.
3. Active Water Treatment Plants
Conventional active treatment plants employ physical, chemical, and biological processes, such as clarification, filtration, precipitation, ion exchange, and reverse osmosis, to remove contaminants from mine water. These systems are highly effective for complex or variable water chemistries and are often used to treat water for discharge or reuse, ensuring compliance with strict environmental standards.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data
IoT-based monitoring systems enhance water management by providing real-time data on water quality and levels. A 2023 study from China demonstrates improved recycling efficiency in coal mines, a model applicable to the USA and Canada. Advanced analytics, predictive maintenance, and automated controls further optimize water handling and early risk detection.
5. Water Treatment and Desalination
In water-scarce regions like the Middle East, desalination and treatment are costly. Minetek’s evaporation systems offer a cost-effective alternative, reducing reliance on chemical treatments. A 2025 Brazilian study emphasizes the integration of desalination with reuse. Additionally, advanced desalination technologies, including reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, and forward osmosis, are increasingly deployed to convert mine-affected water into process water or potable supply.
6. Floating Evaporators
For mines with limited space, floating evaporators provide a compact solution. Minetek’s floating systems maximize efficiency, evaporating up to 50% of processed water volume as pure water vapor, the remaining droplets returning to the pond, and help prevent environmental damage by containing toxic water within the pond while ensuring compliance. Powered by robust electric motors and designed to process varying capacities of water per minute, ensuring comprehensive and efficient water management.
7. Underground Mine Water Storage and Backfilling
Some mining operations use abandoned underground workings as controlled storage reservoirs for excess mine water or as part of cemented paste backfill operations. This approach not only manages water volumes but can also contribute to ground stability and reduce the risk of surface discharge.
8. Artificial Recharge and Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR)
Artificial recharge and ASR involve injecting treated mine water into local aquifers for temporary storage and later recovery. This technology is gaining traction in regions with strict water balance requirements or where seasonal water availability fluctuates, allowing mines to store surplus water during wet periods for use during droughts.